The syndicated loan market is a large funding market for corporate or project financing. The sharing of lending across the syndicate of lenders allows for greater diversification, thereby overcoming individual lenders’ risk, liquidity or other constraints. In this research, we document some key trends in the syndication market, and show how increased network effects appear to be associated with lower lending spreads for large lenders.
Syndication Network Becoming Increasingly Concentrated, Particularly after the 2008 Great Financial Crisis
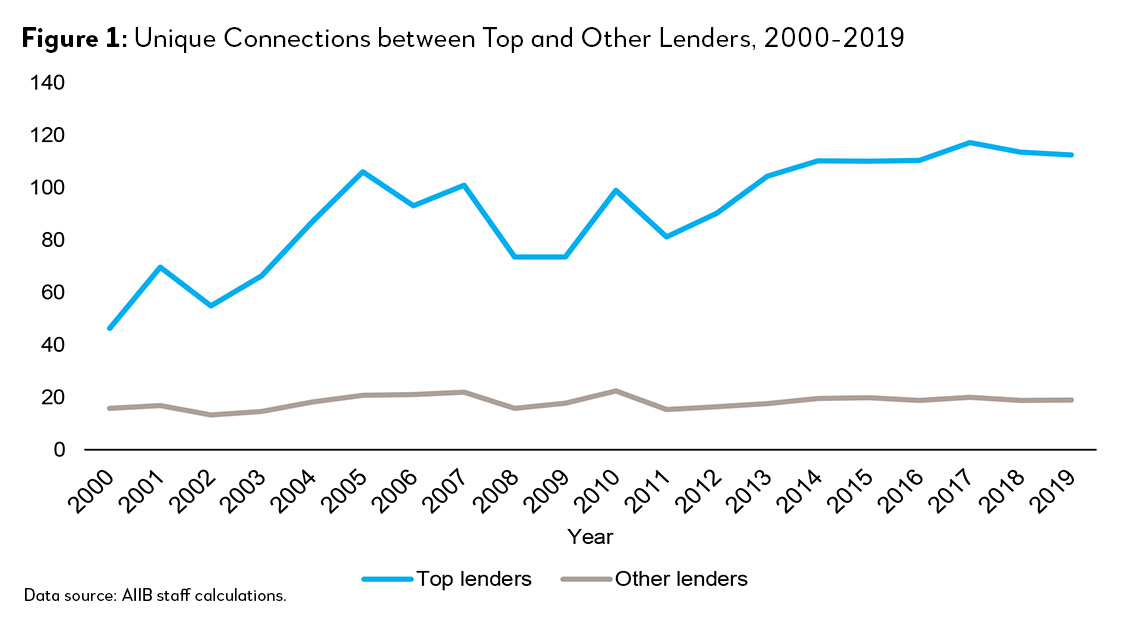
We first show that there has been a growing network concentration in the syndicated loan market, especially after the 2008 Great Financial Crisis (GCF). Figure 1 presents the evolution of the syndication network between 2000 and 2019. We define unique connections as the (non-repeated) number of syndicating relationships with other lenders. To be clear, when Bank A has four syndication deals with Bank B in a year, we count only one unique relationship between Bank A and Bank B. We believe this is a good measure of how extensive a lender’s network is. From Figure 1, it is clear that top lenders have more unique syndicating relationships and have become much more connected.
We also show this through network analysis (Figure 2). Lenders are connected with light blue lines if they participated in the same syndicated deal. Each blue circle denotes a creditor that participates in the syndicated loan market, and its size represents the total number of unique connections the lender has with other creditors in the network. The greater the size of the circles and the closer they are to the center of network, the thicker the concentration of their connections. From 2011, syndicate connections started to disproportionally gather at a few syndicators, as indicated by some extremely large circles. They also tend to be at the center of the network. Besides, connections between these big players also seem be more intense than other connections. Major participants not only gathered the most connections in the entire network but also are connected very closely with other major participants.
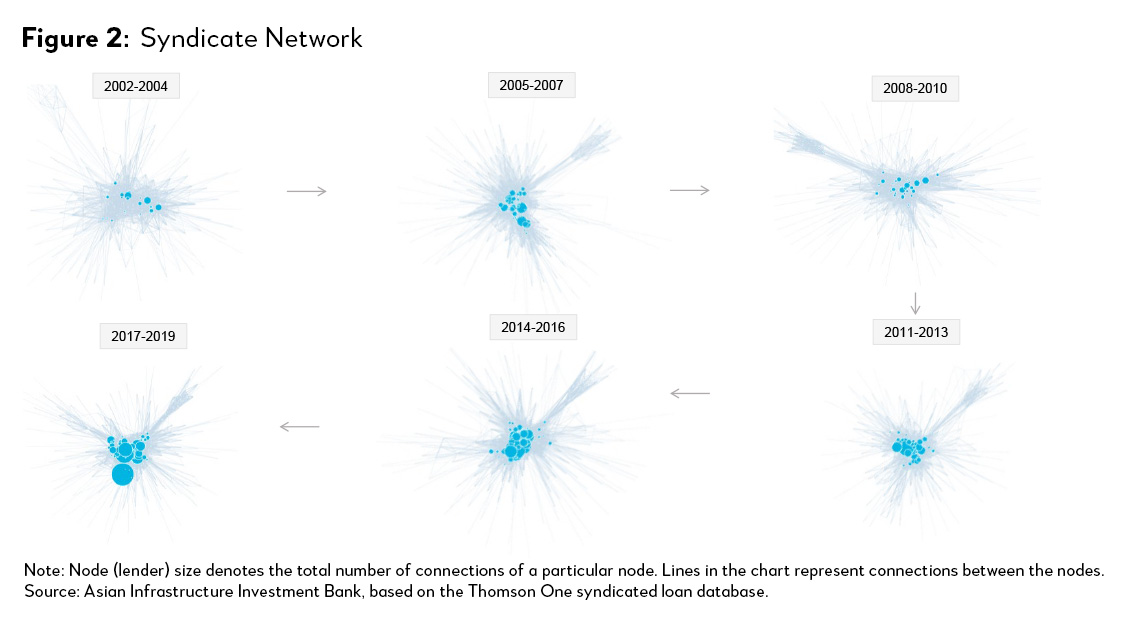
Lenders with concentrated connections include large financial institutions, such as Bank of America Group, JP Morgan Chase, Citi Group, BNP Paribas, etc. These banks dominate the syndicate connections and have remained central to the overall market network for years. One interesting question is how this rising concentration has impacted spreads.
Loans by Well-Connected Lenders Saw Lower Loan Spreads than Small and Less Well-Connected Creditors
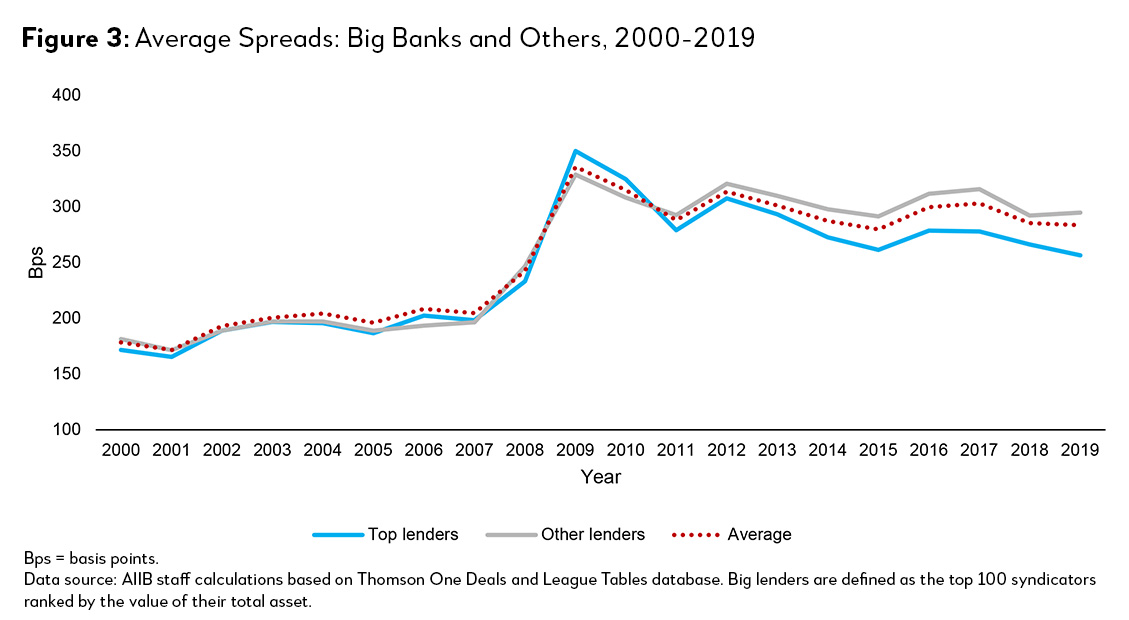
Typically, economists expect that rising industry concentration, or market power, would result in higher markups. In contrast to this economic intuition, loans involving top lenders saw lower interest spreads to the borrowers. Interestingly, such difference seems to have occurred after the GFC.
Post-GFC, spreads charged by both large and small lenders increased considerably due to higher regulatory costs. One of the most important changes is the Basel III requirements for higher capital and liquidity provisions. Other overheads, for example, cyber security requirements and HR-related costs, could have increased as well. Yet spreads rose to a lesser extent among top lenders (Figure 3). In 2019, top lenders recorded around 40 basis points lower spreads for their loans.
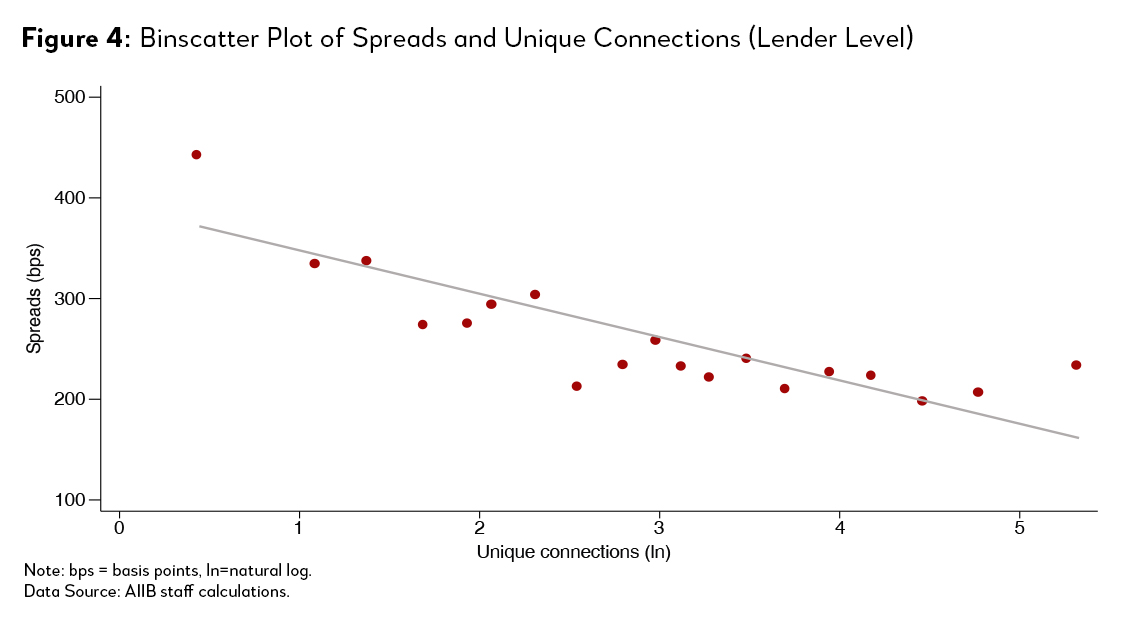
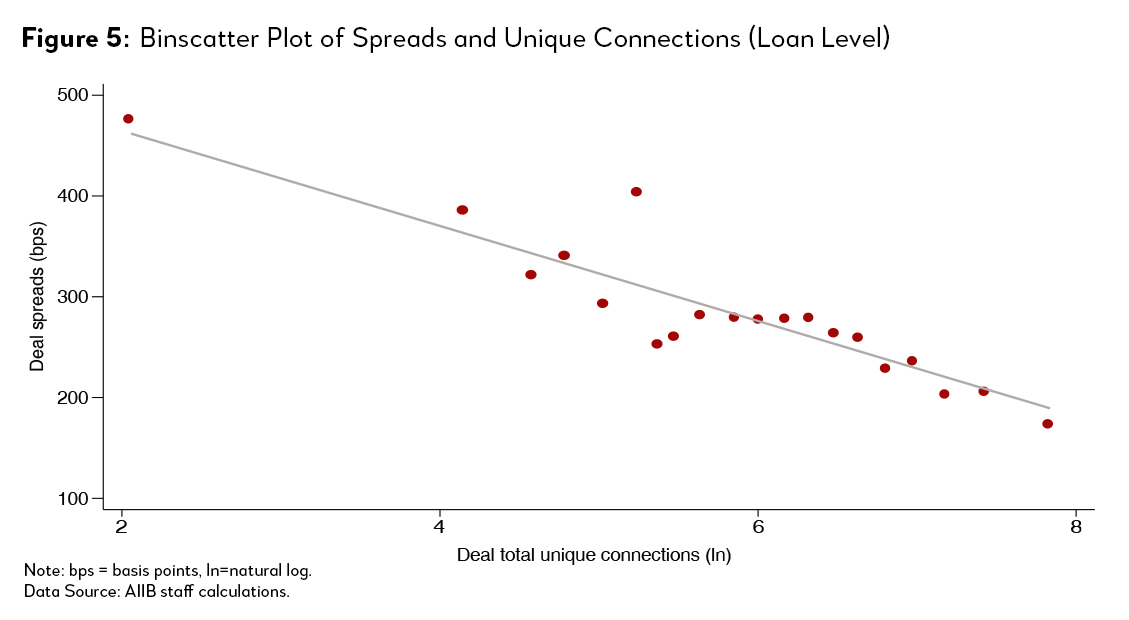
We find that the network effects can explain this difference. Figure 4 shows the scatterplot between number of unique connections of lenders against their average spreads in syndicated loan deals. Lenders with more connections in general have lower spreads. We also check this at the loan level, and the negative relationship between spreads and number of connections of syndicate continues to hold (Figure 5).
The AIIB Working Paper formally tests and quantifies this network effects on loan syndication costs. The conclusion that network connections are associated with lower spreads holds after controlling many other factors including year, sector, firm characteristics (e.g. operating expenses), loan tenor, etc. Consider a lender with about four unique connections a year (25th percentile), versus a lender with 28 unique connections (75th percentile). The spread is about 40 bps lower for latter than the former lender.
Evidence of Beneficial Information Sharing and Diversification Effects through Syndication
The fact that concentrated lenders do not have higher spreads is on the face of it rather good news. This may reflect the fact that information sharing and diversification are indeed helpful in lowering the cost of loans. Finally, it should be noted that one of the key attributes of syndicated loan market is its relative transparency. The competition of the market and the disclosure of information make it difficult for large lenders to charge unreasonable markups, even with their increasing network concentration.
∗ This article is part of a longer discussion on “Increasingly Networked Lenders and Their Impact on Lending Spreads”, a AIIB Working Paper written by the same authors.


